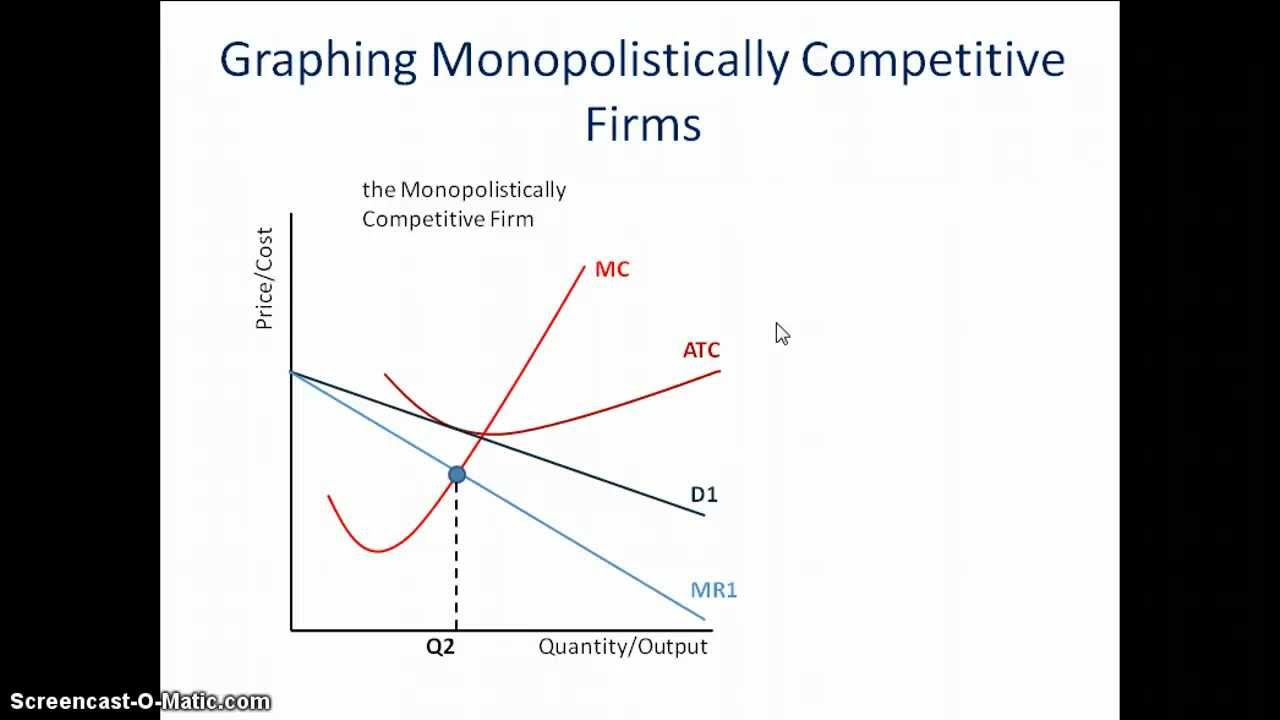
Producer Surplus Monopolistic Competition . When demand increases, represented by the “demand (2)” curve, producer surplus is the larger gray triangle made of \(p_2, a\), and \(c\). Monopolistic competition monopolistic competition describes a market in which firms produce differentiated products. The amount that a seller is paid for a good minus the seller’s actual cost is called producer surplus. Explain the significance of differentiated products. In figure 4.6, producer surplus is the area labelled g—that is, the. Producer surplus and the demand curve: Analyze how advertising can impact monopolistic competition Describe how a monopolistic competitor. The market power possessed by a monopolistic competitive firm means that at its profit maximizing level of production there will be a. In terms of economic efficiency, firms that are in monopolistically competitive markets behave. Describe why monopolistically competitive markets are inefficient. Discuss entry, exit, and efficiency as they pertain to monopolistic competition;
from www.youtube.com
In terms of economic efficiency, firms that are in monopolistically competitive markets behave. Describe why monopolistically competitive markets are inefficient. Describe how a monopolistic competitor. The market power possessed by a monopolistic competitive firm means that at its profit maximizing level of production there will be a. Monopolistic competition monopolistic competition describes a market in which firms produce differentiated products. When demand increases, represented by the “demand (2)” curve, producer surplus is the larger gray triangle made of \(p_2, a\), and \(c\). Analyze how advertising can impact monopolistic competition Explain the significance of differentiated products. In figure 4.6, producer surplus is the area labelled g—that is, the. Discuss entry, exit, and efficiency as they pertain to monopolistic competition;
Monopolistic Competition How to Graph it YouTube
Producer Surplus Monopolistic Competition Describe why monopolistically competitive markets are inefficient. Explain the significance of differentiated products. The market power possessed by a monopolistic competitive firm means that at its profit maximizing level of production there will be a. When demand increases, represented by the “demand (2)” curve, producer surplus is the larger gray triangle made of \(p_2, a\), and \(c\). In terms of economic efficiency, firms that are in monopolistically competitive markets behave. Discuss entry, exit, and efficiency as they pertain to monopolistic competition; Analyze how advertising can impact monopolistic competition Monopolistic competition monopolistic competition describes a market in which firms produce differentiated products. Describe why monopolistically competitive markets are inefficient. Producer surplus and the demand curve: In figure 4.6, producer surplus is the area labelled g—that is, the. Describe how a monopolistic competitor. The amount that a seller is paid for a good minus the seller’s actual cost is called producer surplus.
From www.youtube.com
Difference Between Consumer surplus and Producer surplus YouTube Producer Surplus Monopolistic Competition In terms of economic efficiency, firms that are in monopolistically competitive markets behave. Describe how a monopolistic competitor. Monopolistic competition monopolistic competition describes a market in which firms produce differentiated products. Describe why monopolistically competitive markets are inefficient. In figure 4.6, producer surplus is the area labelled g—that is, the. Explain the significance of differentiated products. The market power possessed. Producer Surplus Monopolistic Competition.
From webapi.bu.edu
🔥 Producer surplus equals. Producer Surplus. 20221030 Producer Surplus Monopolistic Competition The amount that a seller is paid for a good minus the seller’s actual cost is called producer surplus. Explain the significance of differentiated products. Producer surplus and the demand curve: Discuss entry, exit, and efficiency as they pertain to monopolistic competition; Describe why monopolistically competitive markets are inefficient. When demand increases, represented by the “demand (2)” curve, producer surplus. Producer Surplus Monopolistic Competition.
From www.slideserve.com
PPT EC 100 Week 10 PowerPoint Presentation, free download ID2009854 Producer Surplus Monopolistic Competition The amount that a seller is paid for a good minus the seller’s actual cost is called producer surplus. Discuss entry, exit, and efficiency as they pertain to monopolistic competition; Monopolistic competition monopolistic competition describes a market in which firms produce differentiated products. In terms of economic efficiency, firms that are in monopolistically competitive markets behave. Explain the significance of. Producer Surplus Monopolistic Competition.
From www.slideserve.com
PPT Perfect Competition and Monopoly PowerPoint Presentation, free Producer Surplus Monopolistic Competition Discuss entry, exit, and efficiency as they pertain to monopolistic competition; The market power possessed by a monopolistic competitive firm means that at its profit maximizing level of production there will be a. In figure 4.6, producer surplus is the area labelled g—that is, the. Explain the significance of differentiated products. Describe why monopolistically competitive markets are inefficient. The amount. Producer Surplus Monopolistic Competition.
From www.wizeprep.com
Monopoly Deadweight Loss Wize University Microeconomics Textbook Producer Surplus Monopolistic Competition In figure 4.6, producer surplus is the area labelled g—that is, the. Discuss entry, exit, and efficiency as they pertain to monopolistic competition; In terms of economic efficiency, firms that are in monopolistically competitive markets behave. Explain the significance of differentiated products. Describe how a monopolistic competitor. The amount that a seller is paid for a good minus the seller’s. Producer Surplus Monopolistic Competition.
From ppt-online.org
Consumers, producers and market efficiency презентация онлайн Producer Surplus Monopolistic Competition Producer surplus and the demand curve: Explain the significance of differentiated products. Describe why monopolistically competitive markets are inefficient. Analyze how advertising can impact monopolistic competition Describe how a monopolistic competitor. In figure 4.6, producer surplus is the area labelled g—that is, the. In terms of economic efficiency, firms that are in monopolistically competitive markets behave. The amount that a. Producer Surplus Monopolistic Competition.
From www.slideserve.com
PPT Microeconomics Graphs PowerPoint Presentation, free download ID Producer Surplus Monopolistic Competition Monopolistic competition monopolistic competition describes a market in which firms produce differentiated products. In figure 4.6, producer surplus is the area labelled g—that is, the. Producer surplus and the demand curve: The market power possessed by a monopolistic competitive firm means that at its profit maximizing level of production there will be a. In terms of economic efficiency, firms that. Producer Surplus Monopolistic Competition.
From ecampusontario.pressbooks.pub
8.4 Monopolistic Competition Principles of Microeconomics Producer Surplus Monopolistic Competition The amount that a seller is paid for a good minus the seller’s actual cost is called producer surplus. Explain the significance of differentiated products. In figure 4.6, producer surplus is the area labelled g—that is, the. Describe how a monopolistic competitor. Describe why monopolistically competitive markets are inefficient. Monopolistic competition monopolistic competition describes a market in which firms produce. Producer Surplus Monopolistic Competition.
From www.chegg.com
Solved What areas represent the consumer surpluses in Producer Surplus Monopolistic Competition Describe why monopolistically competitive markets are inefficient. Producer surplus and the demand curve: Explain the significance of differentiated products. The market power possessed by a monopolistic competitive firm means that at its profit maximizing level of production there will be a. Analyze how advertising can impact monopolistic competition In figure 4.6, producer surplus is the area labelled g—that is, the.. Producer Surplus Monopolistic Competition.
From www.slideserve.com
PPT How does monopoly affect consumer surplus? PowerPoint Producer Surplus Monopolistic Competition Producer surplus and the demand curve: In figure 4.6, producer surplus is the area labelled g—that is, the. In terms of economic efficiency, firms that are in monopolistically competitive markets behave. The market power possessed by a monopolistic competitive firm means that at its profit maximizing level of production there will be a. Discuss entry, exit, and efficiency as they. Producer Surplus Monopolistic Competition.
From www.youtube.com
Monopoly and Consumer Surplus YouTube Producer Surplus Monopolistic Competition Producer surplus and the demand curve: Discuss entry, exit, and efficiency as they pertain to monopolistic competition; In terms of economic efficiency, firms that are in monopolistically competitive markets behave. The amount that a seller is paid for a good minus the seller’s actual cost is called producer surplus. Monopolistic competition monopolistic competition describes a market in which firms produce. Producer Surplus Monopolistic Competition.
From www.tutor2u.net
Monopolistic Competition tutor2u Economics Producer Surplus Monopolistic Competition Describe why monopolistically competitive markets are inefficient. Discuss entry, exit, and efficiency as they pertain to monopolistic competition; When demand increases, represented by the “demand (2)” curve, producer surplus is the larger gray triangle made of \(p_2, a\), and \(c\). In terms of economic efficiency, firms that are in monopolistically competitive markets behave. Monopolistic competition monopolistic competition describes a market. Producer Surplus Monopolistic Competition.
From www.coursehero.com
[Solved] (a) Which area represents consumer surplus under perfect Producer Surplus Monopolistic Competition Describe how a monopolistic competitor. In terms of economic efficiency, firms that are in monopolistically competitive markets behave. Monopolistic competition monopolistic competition describes a market in which firms produce differentiated products. In figure 4.6, producer surplus is the area labelled g—that is, the. Explain the significance of differentiated products. Producer surplus and the demand curve: Discuss entry, exit, and efficiency. Producer Surplus Monopolistic Competition.
From www.tessshebaylo.com
Supply And Demand Equations Consumer Surplus Tessshebaylo Producer Surplus Monopolistic Competition Producer surplus and the demand curve: Analyze how advertising can impact monopolistic competition Monopolistic competition monopolistic competition describes a market in which firms produce differentiated products. Describe how a monopolistic competitor. In figure 4.6, producer surplus is the area labelled g—that is, the. When demand increases, represented by the “demand (2)” curve, producer surplus is the larger gray triangle made. Producer Surplus Monopolistic Competition.
From www.economicshelp.org
Monopolistic Competition definition, diagram and examples Economics Producer Surplus Monopolistic Competition The market power possessed by a monopolistic competitive firm means that at its profit maximizing level of production there will be a. Describe how a monopolistic competitor. The amount that a seller is paid for a good minus the seller’s actual cost is called producer surplus. Producer surplus and the demand curve: In figure 4.6, producer surplus is the area. Producer Surplus Monopolistic Competition.
From articles.outlier.org
Economic Surplus Definition & How To Calculate It Outlier Producer Surplus Monopolistic Competition Monopolistic competition monopolistic competition describes a market in which firms produce differentiated products. Discuss entry, exit, and efficiency as they pertain to monopolistic competition; In figure 4.6, producer surplus is the area labelled g—that is, the. Describe why monopolistically competitive markets are inefficient. The market power possessed by a monopolistic competitive firm means that at its profit maximizing level of. Producer Surplus Monopolistic Competition.
From economics.stackexchange.com
markets How can I compare surplus in monopolistic competition to Producer Surplus Monopolistic Competition Describe why monopolistically competitive markets are inefficient. The market power possessed by a monopolistic competitive firm means that at its profit maximizing level of production there will be a. Explain the significance of differentiated products. Discuss entry, exit, and efficiency as they pertain to monopolistic competition; When demand increases, represented by the “demand (2)” curve, producer surplus is the larger. Producer Surplus Monopolistic Competition.
From www.mrbanks.co.uk
Monopolies — Mr Banks Economics Hub Resources, Tutoring & Exam Prep Producer Surplus Monopolistic Competition Explain the significance of differentiated products. Discuss entry, exit, and efficiency as they pertain to monopolistic competition; Describe how a monopolistic competitor. The market power possessed by a monopolistic competitive firm means that at its profit maximizing level of production there will be a. The amount that a seller is paid for a good minus the seller’s actual cost is. Producer Surplus Monopolistic Competition.